HELLO! Welcome to My Excuse to Code and Learn TRIGONOMETRY
Mr. Larson, if you’re really seeing this: I want extra credit. Please. This was alot of typing
👉 Click the tabs above to explore: identities, examples, graphing info, and more!

👉 Click the tabs above to explore: identities, examples, graphing info, and more!
csc(θ) = 1/sin(θ)
sec(θ) = 1/cos(θ)
cot(θ) = 1/tan(θ)
tan(θ) = sin(θ)/cos(θ)
cot(θ) = cos(θ)/sin(θ)
sin²(θ) + cos²(θ) = 1
1 + tan²(θ) = sec²(θ)
1 + cot²(θ) = csc²(θ)
sin(a ± b) = sin(a)cos(b) ± cos(a)sin(b)
cos(a ± b) = cos(a)cos(b) ∓ sin(a)sin(b)
tan(a ± b) = (tan a ± tan b) / (1 ∓ tan a tan b)
sin(-θ) = -sin(θ), cos(-θ) = cos(θ), tan(-θ) = -tan(θ)
a/sin A = b/sin B = c/sin C
c² = a² + b² - 2ab cos C
Area = ½ ab sin C
s = rθ, A = ½ r²θ (θ in radians)
General forms:
y = a sin(bx)
y = a cos(bx)
y = a tan(bx)
Amplitude: |a|
Period: 2π / b
sin(θ) = opposite / hypotenuse
cos(θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse
tan(θ) = opposite / adjacent
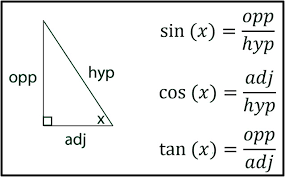
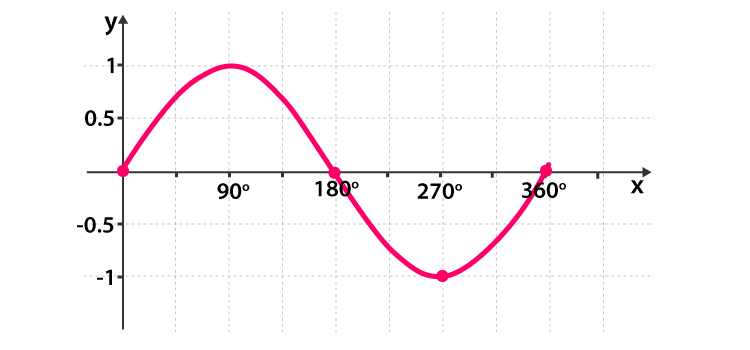
On the unit circle:
sin(θ) = y, cos(θ) = x, tan(θ) = y/x